Linear Regression Acceleration Technical Analysis & Signals
Linear Regression Acceleration calculates the change in the regression line's gradient on the current price bar from its gradient from the previous price bar. The value used to calculate the linear regression is referred to as the normalized acceleration value which is plotted for each price bar formed on the price chart.
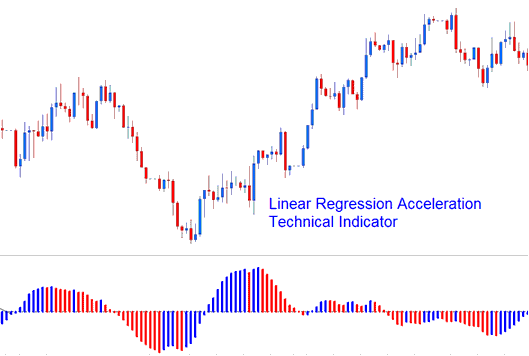
Linear Regression Acceleration
If normalized acceleration is 0.30, then regression line normalized slope will be rising at the rate of 0.30 per price bar.
Similarly, a normalized slope of -0.40 would indicate that the regression line normalized slope is declining at rate of -0.40 per price bar.
For example, if the current price bar normalized slope value is 0.40 and the previous price bar normalized slope value is 0.20, then the normalized acceleration of the current price bar would be calculated as 0.40 - 0.20 = 0.20.
Note: It's important to realize that a positive acceleration value doesn't equate to a positive slope value, it simply means the gradient of slope is increasing. A negative acceleration value doesn't equate to a negative slope value, it simply means the gradient of slope is decreasing.
Implementation of Linear Acceleration Regression Indicator
The Linear Regression Acceleration indicator allows for the following; price selection, regression periods, smoothing of raw price before applying the regression and selection of the smoothing type.
Resulting regression slope is displayed as a bi-colored histogram that oscillates above and below 0.
reference line is set at the 0 level mark.
- A rising slope: (greater than its previous value of 1 bar before) is displayed in up slope color.
- A declining slope: (lower than its previous value of 1 bar before) is shown using the down slope color.
